Briefing
Background
WACKER is the global #2 silicone producer. With silicones being one of the most versatile materials we serve all kind of industries in numerous applications. Together with our customer we constantly develop new applications. However, beside our global market penetration, we suspect unknown applications or emerging technologies where silicone fluids can contribute with their unique properties. We need you to challenge our horizon!
Task
Your task is it to identify and explain new applications (large scale) for non-reactive linear silicon fluids (not crosslinkable in application).
Which problem is solved by your idea? Which value is delivered? In which industry could the technology be applied? Describe the unique selling point opposed to common competitive products.
We do NOT search for ideas to chemically modify silicon fluids.
We expect you to do a short web or literature search. There are so many existing applications of linear fluids out there already!
Properties
WACKER silicone fluids are unique polymers. Their key properties are:

- transparency
- UV stability
- high temperature resistance
- physiologically and chemical inertness
- non-reactive & not crosslinkable
- insolubility in water
- water repellency
- low surface tension
- resistance towards alpha, beta and gamma radiation
Technology
This is due to their unique molecular structure combining an inorganic backbone with organic side groups. The structure of silicone fluids can be represented by the following general formula:
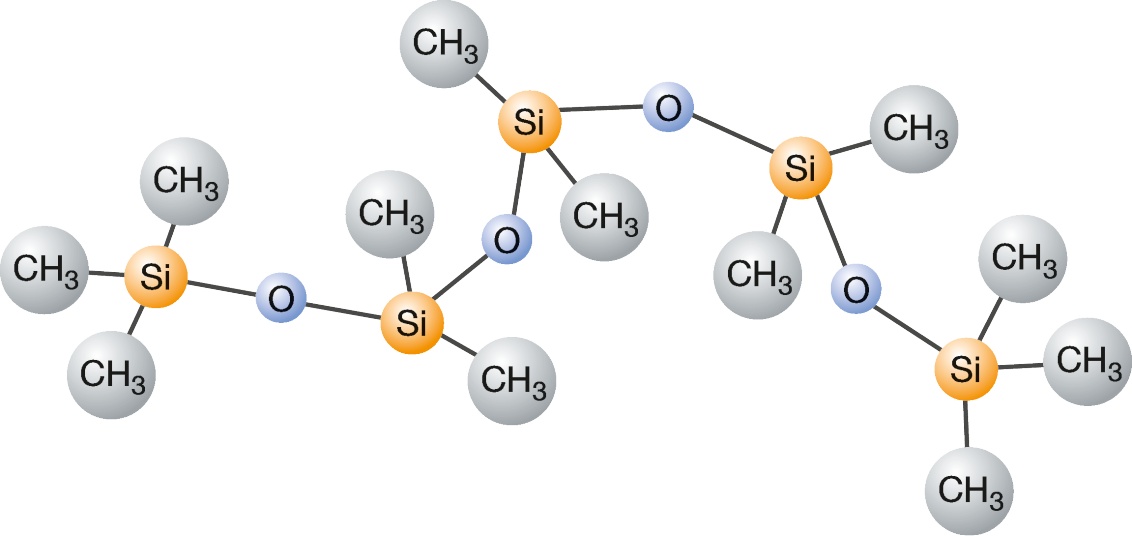
The inorganic Si-O linkage in the backbone causes the high stability, resistance and inertness mentioned above.
Wacker silicone fluids can be supplied in an incredible wide viscosity range from 0.65 to 1.000.000 mm2/s-1 corresponding to a polymer chain length of zero to several thousand repetition units. This is due to their very weak intermolecular forces between the individual chains.
Compared to organic fluids like mineral oils, the unique polymer structure results in
- a very low viscosity-dependency on temperature
- very low melting and pour points
- no shear effect up to 1000 mm2/s-1 (Newtonian liquid)
- non-Newtonian, pseudoplastic behavior for high viscous liquids
- high density-dependence on pressure
- (low surface tension = high surface activity)
- unchanged high electrical insulation properties over a wide variety of frequencies
- high gas solubility (especially an extremely high and pronounced temperature-dependent solubility of CO2)
- extremely high gas permeability
- non-corrosivity
- low fouling potential
Applications and Mode of Action
For these (already existing) applications, silicone fluids can be applied either pure and/or as emulsion.
Release agents
- Demoulding of concrete, rubber and plastics parts, e.g. in aerated concrete and tyre manufacture and in the moulding of polyamide, cellulose acetate, polystyrene and PVC; packaging industry
Lubricants
- Plastics bearings, films, cutting tools, mouldings and extrusions, sewing threads
Damping media
- Speed regulators, fluid clutches (e.g. for fans), nautical and aeronautical instruments, gyrocompasses, shock-absorbing struts, recording instruments, time regulators, pneumatic valves, overload relays, sound pickup
Hydraulic fluids
- Shock absorbers, pumps, brake cylinders
Liquid dielectrics
- Coolants (e.g. for magnetrons and other heat-emitting units), transformers, capacitors, high-voltage tubes, aerospace applications
Water repellents
- Glass, mineral wool, ceramics, laminates; switches, insulators; textiles, leather
Antifoam agents
- Preventing foaming in non-aqueous systems such as mineral and vegetable oils
Creams and polishes
- Car and furniture polishes, shoe creams and floor polishes
Heat transfer fluid
- Long-term resistance up to 150 °C in air; in inert systems up to 425 °C
Cosmetic and dermatological preparations
- Skin-care creams, sun creams, hair-care preparations, insect repellents
Two illustrative extended examples to provide the unique effects that are provided by silicone fluids:

Silicone fluids are widely utilized in all aspects of personal-care product formulation. They are recognized as skin protectant drugs providing a highly gaspermeable barrier on the skin, allowing it to “breath”. Silicone fluids are utilized in skin-care formulations to improve spreading, reduce whitening or soaping during rubbing in, impart softness and provide a breathable, protective barrier on the skin. In hair-care products, silicone fluids reduce combing forces. They also improve the feel of dry hair and reduce “flyaway” as well as imparting humidity resistance and apparent lustre. In sun care and colour cosmetic formulations, silicone fluid with low molecular weight improve spreadability and skin feel, while high molecular weight fluids impart a water-resistant barrier.

The unmatched thermal resistance allows silicon fluids be used as a heat-transfer medium in concentrated solar power (CSP) plants. Silicon fluids can be heated up to 425 °C under inert conditions, thus enabling efficiency levels in the solar power plants that are impossible to achieve with conventional organic heat-transfer media. At the same time, the silicone fluid’s freezing point of -55°C is far lower than that of conventional heat-transfer media. This renders trace heating, which is usually required, unnecessary and thus considerably reduces energy consumption. In addition, fouling, coking and generation of H2 as decomposition product – well known issues with organic heat transfer fluids – are dramatically reduced helping to extend the shelf life of piping and especially of the vacuum isolated receiver. As a result, maintenance expenses decrease and the efficiency of CSP plants increases, in turn making the production of regenerative energy significantly cheaper and more sustainable.
For more information on existing applications you can also browse our product finder.